In today’s rapidly evolving global business landscape, companies face unprecedented challenges in maintaining their competitive edge. Two major trends are reshaping industries worldwide: digital transformation and the rising capabilities of Asian competitors, particularly from China. These developments pose significant threats to the industrial base, especially for German mid-sized companies that have long been global leaders in manufacturing and engineering.
To thrive in this new environment, companies need a comprehensive approach to intellectual property👉 Creations of the mind protected by legal rights. (IP) that goes beyond traditional patent👉 A legal right granting exclusive control over an invention for a limited time. filing. The 360° IP Strategy👉 360° IP strategy aligns all IP types with business, tech, and market goals. offers a systematic framework for leveraging IP as a key driver of innovation👉 Practical application of new ideas to create value., market differentiation, and sustainable profits.
The Changing IP Landscape
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, intellectual property (IP) has become a critical asset for companies seeking to maintain a competitive edge. However, many organizations still struggle to fully leverage their IP portfolios due to outdated perspectives and approaches. This introduction explores the changing IP landscape and common pitfalls that limit the strategic value of IP.
- Equating patents with innovation, leading to a focus on quantity over quality and market relevance: This misconception often results in companies prioritizing patent quantity over strategic value. It can lead to a misallocation of resources, with firms investing heavily in patenting activities that may not align with market needs or business objectives. Additionally, this approach may overlook other forms of IP protection that could be more relevant or valuable in certain situations.
- Viewing IP solely through a legal lens, missing opportunities to use it proactively as a business tool. When IP is treated primarily as a legal matter, companies fail to integrate it into their broader business strategy. This narrow perspective can result in missed opportunities to leverage IP for competitive advantage, revenue generation, or strategic partnerships. Furthermore, it may lead to reactive rather than proactive IP management👉 Strategic and operative handling of IP to maximize value., limiting the potential for IP to drive innovation and growth.
Meanwhile, the competitive landscape has shifted dramatically.
The competitive landscape has undergone a significant transformation in recent years. U.S. tech giants are leveraging strategic patents to establish formidable barriers to entry in digitalized business models, effectively safeguarding their market positions. This approach has made it increasingly challenging for new entrants to compete in the digital space, as they must navigate complex patent landscapes.
Simultaneously, Chinese companies are making remarkable strides in patent filings across core industrial sectors. With growth rates ranging from 120% to 275% in areas such as hydraulics, logistics, and electrical components, Chinese firms are rapidly building their intellectual property portfolios. This surge in patent activity reflects China’s ambition to become a global leader in innovation and technology.
Asian firms are adopting a different strategy by acquiring established Western brands to accelerate their market entry. This approach allows them to quickly gain a foothold in new markets, leveraging existing brand👉 A distinctive identity that differentiates a product, service, or entity. recognition and customer bases. The evolving competitive landscape, characterized by these diverse strategies, has given rise to a new “IP war” that demands a fundamentally different approach – one that aligns IP strategy👉 Approach to manage, protect, and leverage IP assets. directly with business goals and customer needs.
The 4P Concept: Putting the Customer at the Center
The 4P Concept revolutionizes intellectual property strategy by placing the customer at the center of IP management. This innovative approach aligns IP with market-oriented business practices, ensuring that intellectual property directly contributes to customer value and competitive advantage. By integrating four key elements, the 4P Concept creates a powerful framework for leveraging IP to drive business success.
- USP (Unique Selling Proposition): The distinctive value promise to customers.
This element focuses on identifying and articulating the unique benefits that a company’s products or services offer to customers. It requires a deep understanding of customer needs and preferences to develop truly differentiated value propositions. The USP serves as the foundation for building a strong market position and competitive advantage. - UCP (Unique Communication Position): How that value is communicated clearly and memorably.
The UCP translates the USP into compelling messages that resonate with target customers. It involves crafting a clear and memorable communication strategy that effectively conveys the unique value of the company’s offerings. A strong UCP helps cut through market noise and establish a distinct brand identity in customers’ minds. - IP (Intellectual Property): Legal protection creating exclusivity for both the USP and UCP.
This component involves strategically using various forms of intellectual property protection to secure exclusivity for the company’s unique value proposition and communication strategy. It goes beyond traditional patent filing to encompass a comprehensive approach to IP that aligns with business goals. Effective IP protection creates barriers to imitation and helps maintain competitive advantages. - Price Premium: The ability to command higher prices based on perceived unique value.
The culmination of the 4P Concept is the ability to charge premium prices for products or services. This pricing power stems from the perceived unique value created by the USP, effectively communicated through the UCP, and protected by strategic IP. Achieving a price premium directly impacts profitability and reinforces the company’s market position.
This concept builds on the strengths of German mid-sized companies, known as “Hidden Champions”, who excel at deeply understanding customer needs and developing tailored solutions. By explicitly connecting IP to customer value and communication, companies can more effectively leverage their innovations in the marketplace.
Key Principles of the 360° IP Strategy
The 360° IP Strategy represents a paradigm shift in intellectual property management, placing customer value at the core of IP development and utilization. This comprehensive approach aligns IP efforts with business objectives, market dynamics, and customer needs. By integrating IP across all organizational functions and continuously adapting to changing market conditions, companies can create sustainable competitive advantages and maximize the value of their innovations.
- Customer-Centric IP Design👉 IP design is the strategic creation of IP portfolios aligned with business goals.
This principle focuses on developing IP that directly addresses customer needs and preferences. It involves a deep understanding of the market and customer pain points before creating IP. By aligning IP with customer value, companies can protect the most critical aspects of their offerings. This approach ensures that IP investments are strategically focused on areas that drive customer satisfaction and loyalty. - Integrating IP Across the Organization
Integration breaks down traditional departmental barriers to create a unified IP strategy. It encourages collaboration between various teams, fostering a culture of innovation throughout the organization. This holistic approach ensures that IP considerations are embedded in all aspects of business operations. By aligning IP efforts with overall business goals, companies can create more effective and valuable IP portfolios. - Proactive IP Creation
Proactive IP creation involves anticipating future market trends and customer needs. It requires a forward-thinking approach to IP development, focusing on creating exclusivity in key areas. This strategy allows companies to build strong IP positions in emerging markets or technologies. By actively designing IP, companies can create barriers to entry for competitors and secure their market position. - Communicating Value Through IP
This principle emphasizes the importance of leveraging IP in marketing and sales strategies. It involves clearly articulating the unique benefits of protected innovations to customers. Effective communication of IP-protected features can justify premium pricing and differentiate products in the market. This approach helps build brand value and customer loyalty based on unique, protected innovations. - Continuous Alignment with Business Strategy
Continuous alignment ensures that IP strategy remains relevant and effective in a changing business environment. It involves regular review and adjustment of IP portfolios to support evolving business priorities. This principle requires ongoing monitoring of market trends, technological advancements, and competitive landscapes. By maintaining alignment, companies can ensure their IP strategy continues to support long-term business objectives and adapt to new opportunities.
As markets and technologies evolve, IP strategy must be regularly reviewed and adjusted to support changing business priorities and emerging opportunities.
Implementing the 360° IP Strategy
Implementing the 360° IP Strategy requires a systematic approach that aligns intellectual property management with business objectives and customer needs. This comprehensive method involves several key steps, each designed to maximize the value of IP assets and create sustainable competitive advantages. By following these steps, companies can transform their approach to IP, making it a strategic driver of innovation and market success.
- Analyze the Business Model👉 A business model outlines how a company creates, delivers, and captures value.
Start by thoroughly examining your company’s value creation process, identifying key stakeholders and revenue streams. This analysis should include a detailed assessment of your target customers, their needs, and how your offerings meet those needs. Consider your competitive positioning and how IP can enhance your unique value proposition. This foundational step provides the strategic context necessary for making informed IP decisions. - Map the Customer Journey
Create a detailed map of all interactions between your customers and your product or service, from initial awareness to post-purchase support. Identify critical touchpoints where customer satisfaction and loyalty are most influenced. Analyze each stage of the journey to determine where IP can create meaningful differentiation or enhance the customer experience. This mapping process helps prioritize IP efforts and ensures they align with customer-centric business strategies. - Conduct IP Function Deployment
Adapt the Quality Function Deployment methodology to systematically link customer needs with specific IP opportunities. Begin by clearly defining customer requirements and translating them into technical specifications. Identify potential IP protection methods for each specification and evaluate their impact on customer satisfaction. Prioritize IP development efforts based on their potential to create customer value and competitive advantage. - Develop a Knowledge Map
Create a comprehensive inventory of your company’s technical expertise, market insights, and proprietary processes. Categorize this knowledge according to its strategic importance and potential for IP protection. Identify knowledge gaps that may require additional research or acquisition. Use the knowledge map to guide IP strategy, focusing protection efforts on core competencies that drive competitive advantage. - Practice Synthetic Inventing👉 The strategic creation of inventions for IP advantage.
Implement structured brainstorming and problem-solving techniques to systematically generate new IP ideas. Organize cross-functional teams to approach challenges from diverse perspectives. Use tools like TRIZ👉 A systematic problem-solving method using universal inventive principles. (Theory of Inventive Problem Solving) to stimulate creative thinking. Align invention efforts with strategic gaps identified in previous steps to ensure relevance and impact. - Implement IP Controlling
Establish a robust system for monitoring and measuring the business impact of your IP portfolio. Define key performance indicators (KPIs) that link IP assets to business outcomes. Regularly review and analyse these metrics to guide decision-making on IP investments and divestitures. Implement a balanced scorecard approach to ensure a holistic view of IP performance across financial, customer, process, and learning perspectives. - Integrate with Innovation Processes
Embed IP considerations throughout your product development and innovation cycles, from ideation👉 Creative process of generating and developing new ideas. to market launch. Create clear protocols for identifying and evaluating IP potential at each stage of development. Establish cross-functional teams that include IP experts to ensure early and continuous IP input. Develop stage-gate criteria that include IP milestones to guide go/no-go decisions in innovation projects. - Build an IP-aware Culture
Develop a comprehensive training program to educate employees across all levels about the strategic importance of IP. Create incentive systems that reward employees for identifying and developing valuable IP assets. Establish clear communication channels for sharing IP-related information and best practices throughout the organization. Foster a culture of innovation and IP awareness by celebrating IP successes and showcasing their impact on business performance.
Case Studies: The 360° IP Strategy in Action
The 360° IP Strategy has proven its effectiveness across various industries, as demonstrated by several European mid-sized companies. These case studies showcase how aligning intellectual property with customer needs and business objectives can create sustainable competitive advantages. By implementing this comprehensive approach, these companies have successfully leveraged IP to drive innovation, maintain market leadership, and enhance profitability.
- IFM Electronic GmbH
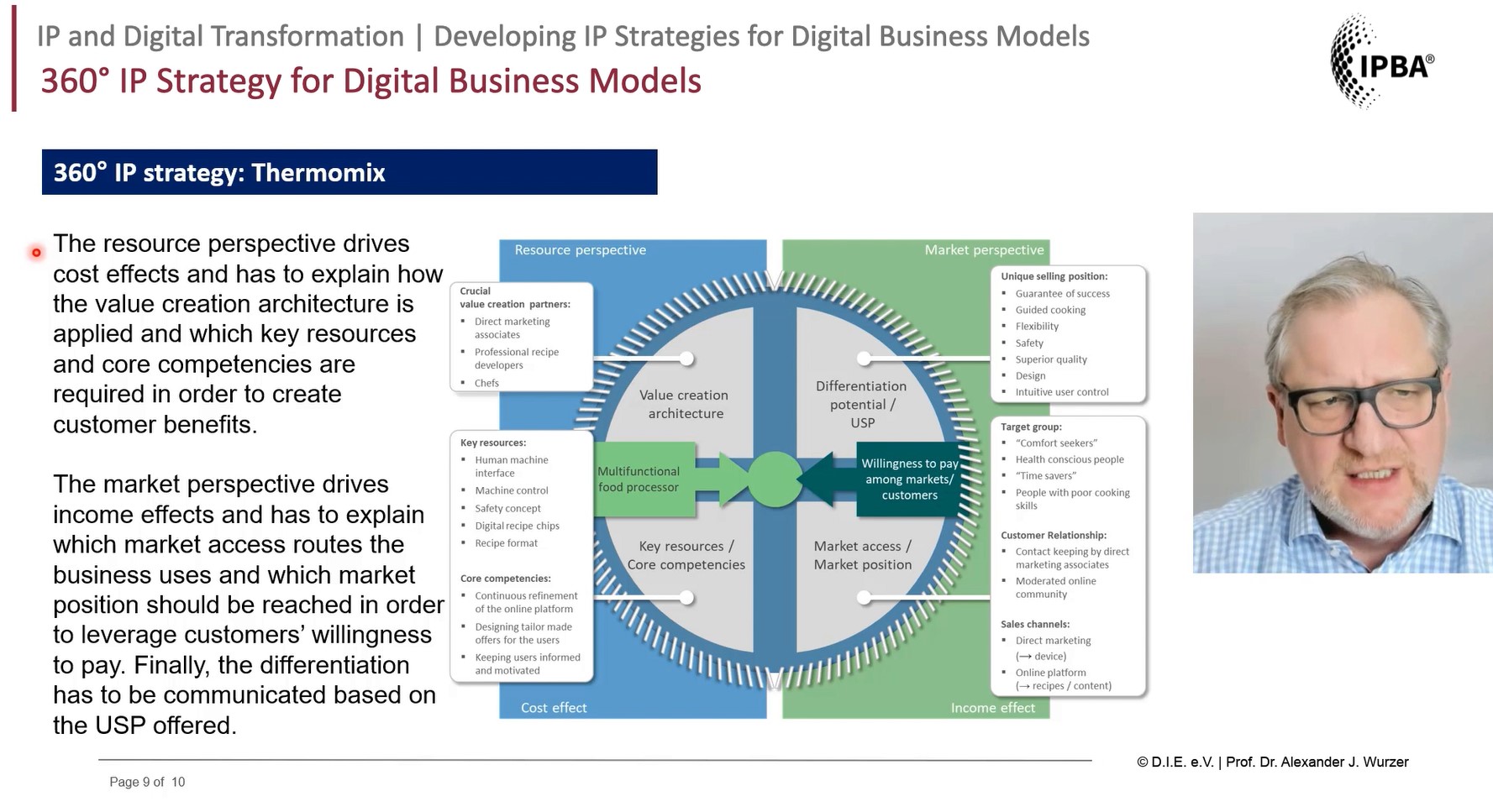
IFM Electronic GmbH revolutionized its innovation process👉 A structured journey of creating and implementing new ideas. by prioritizing customer insights gathered through its global sales network. This customer-centric approach allows the company to identify and address specific market needs more effectively. By systematically analysing customer problems, IFM develops targeted solutions that precisely meet user requirements. The company then backs these innovations with strategic IP protection, creating a strong competitive moat around its customer-focused offerings. - Thermomix (Vorwerk)
Thermomix has implemented a multi-layered IP strategy to maintain its premium position in the kitchen appliance market. The company uses patents to protect its core technologies, ensuring exclusivity for its innovative features. Design rights are employed to safeguard the product’s distinctive appearance, which has become a key part of its brand identity. Trademarks further reinforce the brand and protect the unique user experience associated with Thermomix products. This comprehensive approach creates significant barriers to imitation, allowing Thermomix to maintain its market leadership and premium pricing. - ARRI
ARRI’s success stems from its deep understanding of cinematographers’ needs, which informs its innovation process. The company focuses on creating products that are not only technically advanced but also highly user-friendly, addressing specific pain points in film production. ARRI strategically patents these customer-centric features, protecting the innovations that matter most to its users. This targeted IP strategy allows ARRI to command premium prices in a competitive market, as customers recognize and value the unique benefits offered by its products. - Wilo
Wilo has transformed its IP approach by moving beyond the traditional focus on protecting technical inventions👉 A novel method, process or product that is original and useful.. The company now aligns its IP strategy closely with its digitalization initiatives and service-oriented business model. This integrated approach allows Wilo to create comprehensive “innovation packages” that encompass both physical products and digital services. By protecting these holistic solutions, Wilo makes it difficult for competitors to replicate its offerings. This strategy has positioned Wilo as a leader in the evolving pump industry, where digital capabilities are becoming increasingly important.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Implementing a 360° IP Strategy is a transformative process that demands substantial organizational changes across multiple departments. While the potential benefits are significant, companies often face various hurdles when transitioning to this comprehensive approach. From overcoming internal resistance to developing new competencies, the challenges can be formidable. However, with proper planning and execution, these obstacles can be surmounted, paving the way for a more strategic and value-driven IP management system. Common hurdles include:
- Resistance from traditional R&D and legal departments accustomed to conventional IP practices. R&D and legal teams often struggle to adapt to new IP strategies that challenge their established routines. Overcoming this resistance requires clear communication of the benefits and gradual implementation of changes to allow for adjustment.
- Difficulty in quantifying the business value of strategic IP investments. Measuring the return on investment for IP strategies can be complex, as their impact is often indirect and long-term. Developing appropriate metrics and tracking systems is crucial for demonstrating the value of strategic IP initiatives to stakeholders.
- Lack of IP awareness and skills among marketing and sales teams. Marketing and sales professionals may not fully understand the strategic importance of IP in creating competitive advantages. Targeted training programs and cross-functional collaboration can help bridge this knowledge gap and integrate IP considerations into customer-facing activities.
- Challenges in maintaining a long-term perspective in the face of short-term financial pressures. Companies often prioritize immediate financial results over long-term IP strategies that may not show immediate returns. Balancing short-term goals with the need for sustained IP investment requires strong leadership commitment and clear alignment between IP strategy and overall business objectives.
Successful companies address these challenges through:
- Strong leadership commitment to the new IP approach. Top management’s unwavering support is crucial for driving the cultural shift towards a more strategic IP mindset. Leaders must consistently champion the importance of IP and its alignment with business objectives to ensure organization-wide adoption.
- Pilot projects that demonstrate early wins and build momentum. Carefully selected pilot initiatives showcase the tangible benefits of the new IP strategy, helping to overcome initial scepticism. These early successes create positive momentum and encourage broader acceptance of the strategic IP approach across the organization.
- Comprehensive training programs to develop new IP competencies. Tailored education initiatives equip employees with the necessary skills to effectively implement the new IP strategy. These programs foster a deeper understanding of IP’s strategic value and provide practical tools for integrating IP considerations into daily business activities.
- Revised incentive structures that reward strategic IP creation and utilization. Aligning employee rewards with IP-driven business outcomes encourages active participation in the new approach. These incentives motivate staff to prioritize strategic IP creation and leverage existing IP assets for maximum business impact.
- Implementation of IP management software to improve collaboration and decision-making. Advanced IP management tools streamline processes and enhance visibility across the IP portfolio. These systems facilitate better cross-functional collaboration and provide data-driven insights to support strategic IP decision-making.
The Future of IP Strategy
As industries continue to evolve in an increasingly digitalized world, the 360° IP Strategy must adapt to address emerging trends and technologies, particularly artificial intelligence (AI). The future of IP strategy in this context will likely focus on several key areas:
- Data and Algorithm Protection
As AI and Internet of Things (IoT)👉 “Connected devices exchanging data via internet for smart functionality” technologies mature, protecting data assets and algorithms will become crucial. Companies will need to develop strategies to:- Secure valuable datasets used to train AI models
- Protect proprietary algorithms and machine learning models
- Establish clear data governance policies to maintain control over data assets
- Implement technical measures to prevent unauthorized access or use of data
- Balancing Open Innovation👉 The use of external and internal ideas to drive innovation forward. and Proprietary IP
Companies will need to carefully balance proprietary IP protection with participation in collaborative ecosystems. This may involve:- Developing selective sharing strategies for certain technologies or data
- Creating tiered IP protection approaches based on the strategic importance of assets
- Establishing clear guidelines for employee participation in open source projects
- Leveraging IP to foster partnerships while maintaining competitive advantages
- Sustainability and Circular Economy
IP strategies may increasingly focus on protecting green technologies and circular economy innovations. This could include:- Prioritizing patent filings for environmentally friendly technologies
- Developing IP portfolios around sustainable materials and processes
- Creating licensing👉 Permission to use a right or asset granted by its owner. programs to promote adoption of green innovations
- Collaborating with partners to develop circular economy solutions
- Navigating Global IP Systems
As IP systems become more harmonized yet retain subtle differences, companies will need sophisticated strategies to navigate international regimes. This may involve:- Developing country-specific IP filing and enforcement strategies
- Leveraging international treaties and agreements to streamline global protection
- Building teams with expertise in multiple jurisdictions’ IP laws
- Implementing AI-powered tools to monitor and manage global IP portfolios
- AI-specific Considerations
The rise of AI presents unique challenges and opportunities for IP strategy:- Addressing AI inventorship and ownership issues for AI-generated innovations
- Protecting AI training data and model architectures as trade secrets
- Developing strategies to prevent AI-enabled infringement👉 Unauthorized use or exploitation of IP rights. of existing IP
- Leveraging AI tools for more efficient patent searching and portfolio management👉 Strategic management of diverse assets to optimize returns and balance risk.
- Collaborative IP Management
The future of IP strategy will likely involve more collaborative approaches:- Participating in patent pools and cross-licensing agreements in key technology areas
- Engaging in pre-competitive research collaborations with clear IP frameworks
- Developing IP sharing platforms to facilitate open innovation while maintaining control
- Creating industry standards and best practices for AI and data-related IP issues
By adapting the 360° IP Strategy to address these emerging trends, companies can position themselves to thrive in an increasingly digitalized and AI-driven world. The key will be maintaining a holistic, customer-centric approach to IP while remaining agile in the face of rapid technological change.
Conclusion: IP as a Core Business Function
The 360° IP Strategy represents a fundamental shift in how companies view and utilize intellectual property. By directly linking IP to customer value, market differentiation, and price premiums, it transforms IP management from a specialized legal function into a core driver of business success.
In an era of rapid technological change and intense global competition👉 Rivalry between entities striving for a shared goal or limited resource., this holistic approach to IP offers a powerful tool for companies seeking to secure their innovation leadership. Those who master the 360° IP Strategy will be well-positioned to turn market challenges into opportunities for sustainable growth and profitability.
Implementing this strategy requires commitment, cross-functional collaboration, and a willingness to challenge traditional IP practices. However, as the case studies demonstrate, the potential rewards – in terms of market position, pricing power, and long-term competitive advantage – make it a worthwhile investment for forward-thinking companies.
The 360° IP Strategy is not a one-time project, but an ongoing process of aligning intellectual property with evolving business needs and market dynamics. By continuously refining this approach, companies can build a robust innovation engine that consistently delivers value to customers and shareholders alike.