The digital transformation is reshaping industries and economies worldwide, driven by rapid technological advancements and changing business paradigms. This profound shift goes beyond mere digitization, fundamentally altering how organizations create value, interact with customers, and compete in the marketplace. As we dive into the characteristics of this transformation, we’ll explore its key drivers, impacts, and the new realities it presents for businesses and society at large.
The Driving Forces: Moore’s, Nielsen’s and Metcalfe’s Law
The digital transformation is propelled by several key technological and economic forces. Three laws in particular help explain the rapid pace and far-reaching impacts of this transformation.
- Moore’s Law
Moore’s Law, formulated by Intel co-founder Gordon Moore in 1965, observes that the number of transistors on a microchip doubles about every two years, while the cost halves. This has led to exponential increases in computing power and decreases in cost, enabling the proliferation of digital devices and technologies. The effects of Moore’s Law can be seen in the dramatic improvements in capabilities of smartphones, computers, and other digital technologies over relatively short timeframes. - Nielsen’s Law
Nielsen’s Law, proposed by Jakob Nielsen, states that network connection speeds for high-end users increase by 50% per year. This rapid growth in bandwidth and connectivity has enabled increasingly data-intensive applications and services, from high-definition video streaming to cloud computing. The combination of more powerful devices and faster networks has created the foundation for many transformative digital technologies and business models. - Metcalfe’s Law
Metcalfe’s Law, attributed to Ethernet inventor👉 A person who creates new devices, methods, or processes. Robert Metcalfe, states that the value of a telecommunications network is proportional to the square of the number of connected users. This law helps explain the power of network effects👉 Network effects occur when a product’s value increases as more people use it., where services become more valuable as more people use them. Social media platforms, online marketplaces, and other digital platforms have leveraged these network effects to achieve rapid growth and market dominance.
Together, these three laws create a self-reinforcing cycle of technological advancement, connectivity, and value creation that is a key driver of digital transformation. As devices become more powerful, networks faster, and user bases larger, new possibilities for innovation👉 Practical application of new ideas to create value. and disruption emerge across industries.
Digitization, Digitalization & Digital Transformation
While often used interchangeably, the terms digitization, digitalization, and digital transformation refer to distinct but related concepts in the evolution of technology adoption by businesses and society.
- Digitization
Digitization is the process of converting analog information into digital form. This includes activities like scanning paper documents, converting analog audio and video to digital formats, or replacing analog instruments with digital sensors. Digitization is a foundational step that makes information accessible and manipulable by computer systems. - Digitalization
Digitalization refers to the use of digital technologies and digitized data to improve or transform business processes. This goes beyond simply digitizing information to leveraging digital capabilities to optimize operations, enhance productivity, or create new ways of doing business within existing paradigms. Examples include implementing digital document management systems, using data analytics to inform decision-making, or adopting e-commerce platforms. - Digital Transformation
Digital transformation represents a more fundamental reimagining of business models, products, and services enabled by digital technologies. It involves rethinking how an organization creates and delivers value in the digital age. This may include developing entirely new digital products or services, creating platform-based business models, or fundamentally changing how a company interacts with customers and partners.
The progression from digitization to digitalization to digital transformation reflects increasing levels of organizational change and potential impact. While digitization and digitalization can offer significant efficiency gains and incremental improvements, true digital transformation has the potential to disrupt industries and create entirely new sources of value.
Successful digital transformation requires more than just implementing new technologies. It demands a shift in organizational culture, mindset, and capabilities. Companies must be willing to challenge long-held assumptions, experiment with new approaches, and continuously adapt to rapidly changing digital landscapes.
Network Economy
The network economy, also known as the digital economy or internet economy, refers to the economic activities and value creation enabled by digital networks, particularly the internet. This new economic paradigm is characterized by several key features that distinguish it from traditional industrial economies.
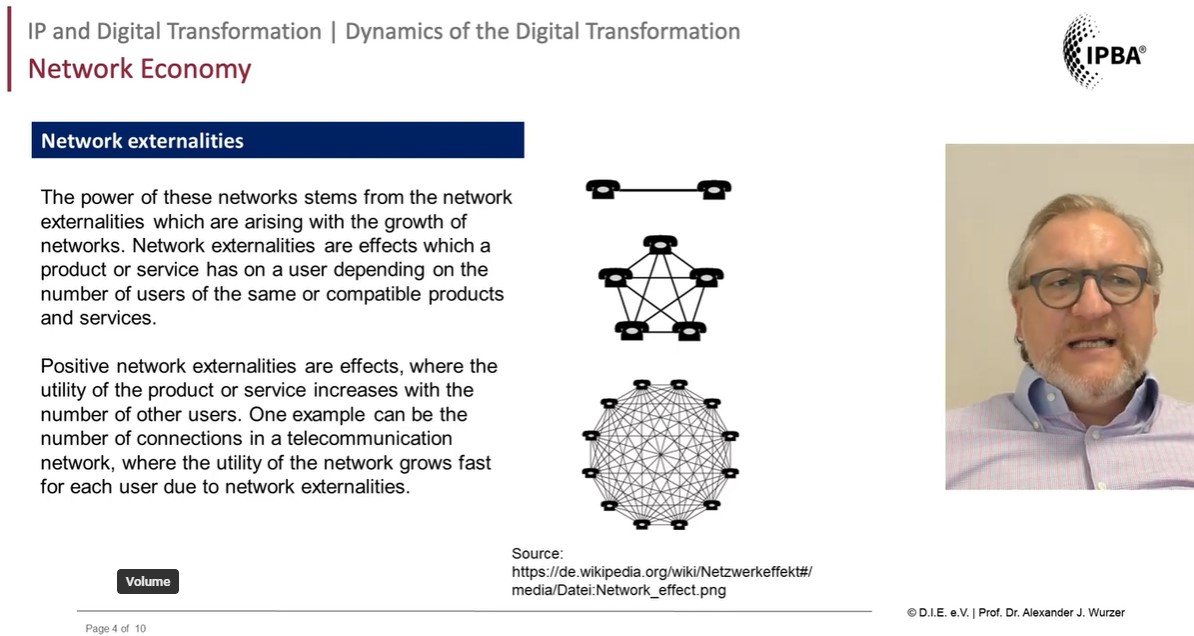
One of the defining characteristics of the network economy is the importance of network effects. As described by Metcalfe’s Law, the value of networks grows exponentially as more users or nodes are added. This dynamic has allowed digital platforms like social media networks, online marketplaces, and sharing economy services to achieve rapid growth and establish dominant market positions.
The network economy is also marked by increasing returns to scale. Unlike physical goods, digital products and services often have very low marginal costs of production and distribution. This allows successful digital businesses to scale rapidly and achieve outsized returns. Companies like Google, Amazon, and Facebook have leveraged this dynamic to become some of the world’s most valuable corporations.
Information and data play a central role in the network economy. Data has been called the “new oil” of the digital age, reflecting its importance as a source of value and competitive advantage. Companies that can effectively collect, analyze, and leverage data can gain significant insights into customer behavior, optimize operations, and create personalized products and services.
The network economy has also led to the rise of platform business models. These multi-sided platforms create value by facilitating interactions between different user groups, such as buyers and sellers on e-commerce platforms or riders and drivers in ride-sharing services. Platform businesses can achieve powerful network effects and often benefit from winner-take-most dynamics in their markets.
Collaboration and open innovation👉 The use of external and internal ideas to drive innovation forward. are more prevalent in the network economy. Digital technologies enable new forms of cooperation across organizational and geographic boundaries. Open-source software👉 Freely accessible code that can be used, modified, and shared. development, crowdsourcing, and collaborative online communities are examples of how networked systems can harness collective intelligence and resources.
The pace of change in the network economy is rapid and often unpredictable. Digital technologies enable fast iteration and experimentation, allowing new products and business models to emerge and scale quickly. This creates both opportunities and challenges for businesses, which must be agile and adaptive to thrive in this environment.
While the network economy offers tremendous opportunities for value creation and innovation, it also presents challenges. Issues such as data privacy, digital divides, platform monopolies, and the disruption of traditional industries and jobs are ongoing concerns that society and policymakers must grapple with.
Digital Eco-Systems, Platforms and the Inverted Firm
Digital ecosystems are complex networks of interconnected organizations and individuals that interact to create and exchange value. These ecosystems, often built around digital platforms, are reshaping industries and challenging traditional notions of firm boundaries and value creation.
At the heart of many digital ecosystems are platform businesses. These platforms act as intermediaries, facilitating interactions between different user groups. For example, ride-sharing platforms connect drivers with passengers, while e-commerce platforms connect sellers with buyers. The platform owner provides the technological infrastructure, sets the rules of engagement, and often monetizes the interactions or data generated within the ecosystem.
Digital ecosystems and platforms are characterized by their ability to scale rapidly and create value through network effects. As more participants join the ecosystem, it becomes more valuable for all users, creating a virtuous cycle of growth. This dynamic allows successful platforms to achieve dominant market positions quickly.
The rise of digital ecosystems has led to the concept of the “inverted firm.” In traditional industrial-era companies, value was created through a linear value chain👉 A series of activities that create and deliver value in a product for end-users., with the firm controlling most aspects of production and distribution. In contrast, platform-based companies often create value by orchestrating resources and interactions that occur outside their direct control.
This inversion of the firm has several implications:
- Reduced asset intensity: Platform companies often achieve high valuations and revenues with relatively few physical assets. Their value lies in their network of users and the data they generate.
- Blurred boundaries: The lines between employees, customers, and suppliers become less distinct in digital ecosystems. Users may play multiple roles, such as being both consumers and producers of content on social media platforms.
- Ecosystem governance: Instead of managing internal hierarchies, platform companies focus on governing their ecosystems through rules, incentives, and technological infrastructure.
- Innovation at the edges: Much of the innovation in digital ecosystems occurs at the periphery, driven by third-party developers, complementors, and users, rather than being centrally controlled by the platform owner.
- Data as a key asset: The ability to collect and analyze data from ecosystem interactions becomes a crucial source of competitive advantage and value creation.
Digital ecosystems and platforms are not limited to consumer-facing industries. In the industrial sector, companies are creating platforms that connect machines, devices, and systems in the Internet of Things (IoT)👉 “Connected devices exchanging data via internet for smart functionality”. These industrial platforms enable new services like predictive maintenance, optimize operations, and create new business models based on data and connectivity.
The ecosystem approach is also changing how companies innovate and compete. Rather than trying to do everything in-house, firms are increasingly focusing on their core competencies and leveraging partnerships within their ecosystems to deliver comprehensive solutions. This requires new approaches to strategy, focusing not just on individual firm capabilities but on the health and competitiveness of the entire ecosystem.
However, the rise of digital ecosystems and powerful platforms also raises concerns. The winner-take-most dynamics of many digital markets have led to the emergence of dominant platforms with significant market power. This has sparked debates about competition👉 Rivalry between entities striving for a shared goal or limited resource. policy, data privacy, and the societal impacts of these new forms of economic organization.
As digital transformation continues to reshape industries, understanding and effectively participating in digital ecosystems will be crucial for business success. Companies must carefully consider their roles within these ecosystems, whether as platform providers, complementors, or hybrid players straddling multiple positions. They must also develop new capabilities in areas such as ecosystem orchestration, data analytics, and rapid innovation to thrive in this new landscape.
The digital transformation, driven by technological advancements and new economic dynamics, is fundamentally altering how businesses operate and create value. From the exponential improvements in computing power and connectivity to the rise of platform-based business models and digital ecosystems, this transformation presents both immense opportunities and significant challenges. As organizations navigate this rapidly evolving landscape, they must embrace new ways of thinking, operating, and competing to succeed in the digital age.
Consequences of the Digital Transformation
The digital transformation is reshaping industries, economies, and societies worldwide. Its consequences are far-reaching, impacting competition, business models, growth, and corporates. Digital transformation is fundamentally altering how businesses operate, compete, and create value. Companies that successfully navigate this shift are seeing significant benefits in productivity, revenue growth, and market positioning. However, the transformation also presents challenges, particularly for legacy organizations, and requires a strategic approach to fully capitalize on the opportunities presented by the digital economy.
Competition and Competitiveness
Digital transformation has indeed significantly altered the competitive landscape:
- Companies fully embracing digital technologies can see productivity increases of up to 40%. This significant boost in productivity demonstrates the transformative power of digital technologies when implemented comprehensively across an organization.
- Organizations that prioritize data-driven decision-making are 5-6% more productive than their competitors. By leveraging data analytics and insights, these companies can make more informed decisions, leading to improved efficiency and effectiveness in their operations.
- A 2022 survey revealed that 71% of executives believe a digital-first strategy is crucial for gaining a competitive edge. This widespread belief among business leaders underscores the importance of prioritizing digital initiatives to stay ahead in today’s rapidly evolving business landscape.
- Digital transformation enables companies to respond more rapidly to market changes and tailor offerings to specific consumer needs. This increased agility and personalization capability allows businesses to better meet customer expectations and adapt quickly to shifting market dynamics.
However, not all companies are benefiting equally from digital transformation:
- Around 70% of digital transformation initiatives fail to achieve their desired results. This high failure rate highlights the complexity and challenges involved in successfully implementing digital transformation strategies, emphasizing the need for careful planning and execution.
- Legacy organizations often struggle with outdated systems and resistance to change. These established companies face significant hurdles in adapting to the digital landscape, as they must not only update their technological infrastructure but also overcome internal cultural barriers and entrenched processes that impede innovation and agility.
The impact of digital transformation on competitiveness is further illustrated by these points:
- Companies that fully embrace digital transformation can achieve revenue growth rates that are 5 to 15% higher than their competitors. This significant boost in revenue growth demonstrates the substantial financial benefits that can be realized through comprehensive digital transformation initiatives.
- Organizations adopting digital transformation can expect to see an increase in revenue by up to 25%. This impressive potential for revenue growth highlights the transformative power of digital technologies in driving business success and market competitiveness.
- Businesses that implement digital technologies can experience a 10% increase in employee productivity. This productivity boost illustrates how digital tools and processes can enhance workforce efficiency, enabling employees to accomplish more in less time.
- Companies using productivity management software see an average increase of 20-30% in overall business productivity. This substantial improvement in productivity underscores the value of specialized digital tools in streamlining operations and optimizing organizational performance.
These statistics highlight the significant potential for digital transformation to enhance competitiveness, but also underscore the challenges many organizations face in successfully implementing these changes.
Business Models and Growth
Digital transformation is revolutionizing how businesses operate and create value. By leveraging new technologies, companies are reimagining their business models, enhancing efficiency, and unlocking unprecedented growth opportunities in an increasingly connected world. Digital transformation is reshaping business models and driving growth:
- Companies fully embracing digital transformation can achieve 5-15% higher revenue growth rates than competitors. This increase in revenue growth underscores the critical role that digital technologies play in enhancing operational efficiency and market responsiveness, allowing these companies to capitalize on new opportunities more effectively.
- Organizations adopting digital transformation can expect revenue increases of up to 25%. This potential for significant revenue growth highlights the transformative impact of digital initiatives on business performance, enabling firms to innovate and expand their offerings in a competitive marketplace.
- E-commerce has become crucial, with Shopify merchants seeing a 200% average increase in online sales during the pandemic. This surge in online sales illustrates how businesses that adapt to digital platforms can rapidly scale their operations and reach a broader customer base, particularly during times of market disruption.
- New revenue models like subscription-based services are emerging, enhancing customer loyalty and revenue stability. By shifting to subscription models, companies can create predictable revenue streams while fostering deeper relationships with customers through ongoing engagement and personalized offerings.
Company Strategies
In the era of digital transformation, companies are revolutionizing their strategies to maintain competitiveness. These new approaches focus on leveraging technology, embracing innovation, and adapting to rapidly changing market dynamics. To remain competitive, companies are adopting new strategies:
- Investing in innovation and digitization to enhance efficiency and upgrade client touchpoints. Companies are allocating significant resources to develop and implement cutting-edge digital technologies that streamline operations and improve customer interactions. This strategic focus on innovation allows businesses to stay competitive by offering more efficient services and creating seamless, modern experiences for their clients.
- Focusing on customer-centric approaches, leveraging digital tools for personalized solutions. Organizations are increasingly utilizing digital platforms and data analytics to gain deeper insights into customer preferences and behaviors. This customer-centric strategy enables companies to tailor their products and services to individual needs, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Embracing agility to swiftly adapt to market fluctuations and evolving customer expectations. Companies are adopting flexible organizational structures and processes that allow them to quickly respond to changing market conditions and customer demands. This agile approach helps businesses remain relevant and competitive in rapidly evolving industries, ensuring they can pivot strategies and offerings as needed.
- Leveraging global reach and accessibility through e-commerce and cloud platforms. Businesses are expanding their market presence by utilizing e-commerce platforms to reach customers worldwide, transcending geographical boundaries. Cloud technologies are enabling companies to scale operations efficiently, provide seamless services, and collaborate globally, enhancing their competitive edge in the international marketplace.
- Prioritizing data analytics for improved decision-making and customer acquisition/retention. Companies are investing heavily in advanced analytics capabilities to extract actionable insights from vast amounts of data, enabling more informed and strategic decision-making. By leveraging these data-driven insights, businesses can optimize their marketing efforts, enhance customer experiences, and develop targeted strategies for acquiring and retaining customers.