Generative AI tools and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) systems are poised to revolutionize the patent search👉 A systematic review of patents literature. process. It is imperative for patent👉 A legal right granting exclusive control over an invention for a limited time. professionals, researchers, and decision-makers in the intellectual property👉 Creations of the mind protected by legal rights. (IP) domain to stay ahead of the curve and understand the implications of these technologies.
The ability to efficiently and accurately search for relevant patents is paramount in today’s competitive environment. AI technologies offer unprecedented opportunities to enhance the patent search process, streamline workflows, and improve decision-making. By understanding and utilizing AI effectively, patent professionals can ensure they remain at the forefront of innovation👉 Practical application of new ideas to create value. in the field of intellectual property.
Understanding AI and RAG
AI tools, particularly generative AI, employ advanced machine learning algorithms to analyze data, generate human-like text, and automate tasks. This can significantly enhance efficiency and accuracy across various stages of the patent search process.
RAG systems combine the power of generative models with retrieval systems, allowing access to external databases and knowledge bases in real-time. This ensures that the information generated is both accurate and current. The integration of generative AI and RAG into existing patent search processes offers unique opportunities for patent professionals.
Exploring AI Tool Variety
AI tools can be broadly classified into online and local models. Online models, such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT-4 and Google’s Gemini, are accessible via cloud-based services and are trained on massive datasets. These models offer powerful capabilities but raise concerns about data security and confidentiality.
Local models, like Meta’s LLaMA 3, are installed and run on individual machines or private servers, offering greater control over data. The choice between online and local models depends on factors such as data security, confidentiality, and resource availability.
Selecting and Using AI Tools
Selecting the right AI tools requires careful consideration of factors such as specific needs, data security requirements, and resource constraints. Effective use of these tools necessitates a blend of technical skills and domain expertise. Understanding advanced prompting techniques is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of AI tools.
Additionally, while non-patent-specific tools offer cost-effectiveness and versatility, they may lack domain-specific knowledge and pose data privacy risks. Organizations must carefully evaluate the trade-offs between leveraging powerful online models and maintaining data security.
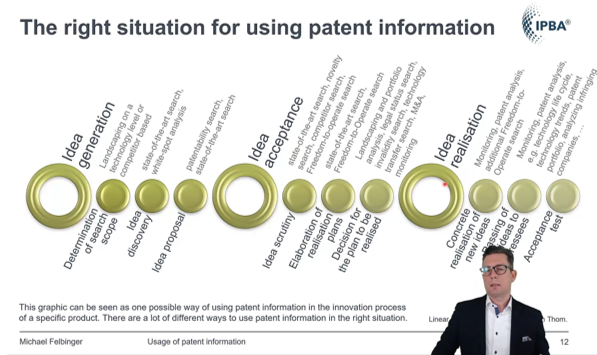
Here is an excerpt from Michael Felbinger’s lecture on patent research:
Who Should Take Note
The integration of AI into patent searching has profound implications for a wide range of stakeholders. Patent professionals, IP specialists, legal teams, R&D departments, and decision-makers in innovation-driven organizations must understand these advancements to remain competitive.
For those seeking to delve deeper into this transformative topic, Michael Felbinger will be giving a lecture at this year’s IP Service World. This lecture will provide further insights into the opportunities and challenges of integrating AI into patent search processes. Don’t miss this chance to enhance your understanding and stay ahead in the rapidly evolving landscape of intellectual property.
Get in contact with Michael
Join Michael at the IP service world to learn all about the interplay between human and artificial intelligence in patent searches. Benefit from Michael’s experience and insights as you make your next patent search decisions.
To get in contact with Michael you can simply send him an email.
Or use this form to give him feedback on your interests or your specific questions: