The chemical industry thrives on innovation, constantly pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with matter. This innovation leads to new compounds, novel processes, and creative applications of existing chemicals. Patent protection plays a crucial role in securing these advancements, providing inventors with exclusive rights to their creations. But what exactly can be patented in this diverse and complex field?
Composition of Matter: The Foundation of Chemical Invention
At the heart of chemical innovation lies the composition of matter itself. This encompasses the discovery and creation of new molecules, compounds, and formulations with unique properties and applications. Patents for composition of matter are fundamental in the chemical industry, protecting the very building blocks of new technologies. This includes:
New Chemical Entities
This covers novel molecules with a defined structure and composition. Think of new drug molecules with therapeutic effects, novel pesticides with improved efficacy, or new polymers with enhanced properties. Patenting these entities protects the specific arrangement of atoms, giving the inventor exclusive rights to manufacture and use the compound.
Isomers and Stereoisomers
Molecules with the same chemical formula but different spatial arrangements of atoms can exhibit vastly different properties. For example, one isomer of a drug might be effective while another is inactive or even harmful. Patents can protect specific isomers or stereoisomers with unique characteristics, ensuring that the inventor can control the specific form with the desired properties.
Polymorphs and Crystalline Forms
A single compound can exist in different crystalline forms, each with unique physical properties like solubility, stability, and bioavailability. For instance, a drug might be more effective in a particular crystalline form. Patents can protect specific polymorphs with advantageous characteristics, allowing the inventor to control the most beneficial form of the compound.
Compositions with Specific Ratios
Mixtures or formulations with defined proportions of different components can also be patented if they exhibit unexpected or synergistic properties. This might include a new paint formulation with improved durability, a new adhesive with enhanced bonding strength, or a new pharmaceutical formulation with increased bioavailability.
Processes and Methods of Use: Beyond the Molecule
Patent protection in the chemical industry extends beyond the composition of matter itself. It also covers the processes used to create these new materials and the methods for their application. This includes:
Methods of Synthesis
Developing a new chemical often involves devising new or improved synthesis methods. This could involve new reaction pathways, catalysts, or purification techniques. Patents can protect these innovative methods of synthesis, ensuring that the inventor has exclusive rights to the most efficient and effective ways to produce the compound.
Manufacturing Processes
Scaling up chemical production from the lab to an industrial scale often requires specialized equipment and optimized processes. Patents can protect these innovative manufacturing methods, covering aspects like continuous flow processes, reactor design, and process control strategies.
Methods of Use
Discovering a new use for an existing or novel chemical can be a valuable invention. This could involve finding a new therapeutic application for a known drug, identifying a new use for an existing polymer, or discovering a new catalytic application for a known compound. Patents can protect these new and non-obvious applications, expanding the potential market for a chemical entity.
Formulations and Mixtures
Combining different chemicals in specific ways can lead to new and improved products. This could include a new drug formulation with enhanced stability or a new adhesive with improved adhesion properties. Patents can protect these specific combinations of chemicals, ensuring that the inventor has exclusive rights to the unique formulation.
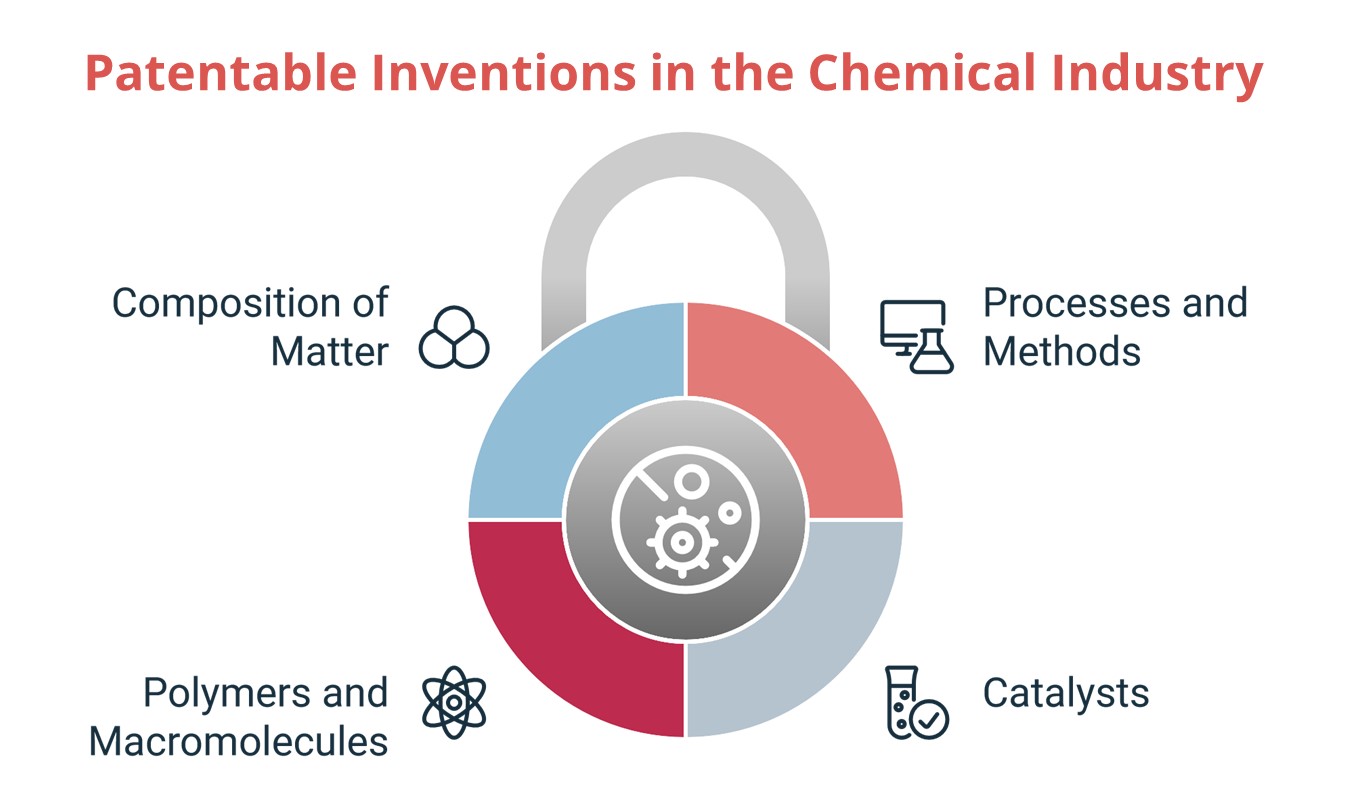
Polymers and Macromolecules: Protecting the Giants
Polymers and macromolecules, including plastics, resins, and fibers, play a vital role in various industries. Patent protection for these materials encompasses:
Composition and Structure
Patents can protect the specific building blocks (monomers) used to create a polymer, the arrangement of these monomers, and the polymer’s overall architecture. This could include new types of polymers with unique properties, new ways of arranging monomers within a polymer chain, or new methods for controlling the polymer’s molecular weight and branching.
Manufacturing Processes
Creating polymers often involves specialized techniques for polymerizing monomers and controlling the polymer’s properties. Patents can protect these manufacturing processes, including methods for controlling molecular weight distribution, introducing specific functional groups, or modifying the polymer’s physical properties.
Applications
Finding new and innovative uses for polymers is a key driver of innovation in this field. Patents can protect these new applications, whether it’s using a new polymer in a medical device, developing a new type of plastic for packaging, or creating a new fiber for textiles.
Catalysts: The Engines of Chemical Reactions
Catalysts are essential in many chemical processes, accelerating reaction rates and improving efficiency. Patent protection for catalysts includes:
Composition and Structure
This covers the specific materials used to create a catalyst, including metals, metal oxides, and organic compounds, as well as their physical form and morphology. This could include new types of catalysts with improved activity, selectivity, or stability.
Methods of Preparation
Synthesizing and activating catalysts often involves specialized techniques. Patents can protect these methods of preparation, ensuring that the inventor has exclusive rights to the most effective ways to produce the catalyst.
Applications
Patents can protect the use of specific catalysts in various chemical reactions, including those relevant to pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, and environmental remediation. This ensures that the inventor can control the use of the catalyst in specific applications where it offers significant advantages.